研究成果53
Tunable photoluminescence from the visible to near-infrared wavelength region of non-stoichiometric AgInS2nanoparticles
Meilin Dai, Shoji Ogawa, Tatsuya Kameyama, Ken-ichi Okazaki, Akihiko Kudo, Susumu Kuwabata, Yasuyuki Tsuboi and Tsukasa Torimoto
J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 12851


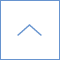
Absorption spectra (a) and PL emission spectra (b) of OLA-AIS nanoparticles. The excitation wavelength in PL spectra was 430 nm. The numbers in the figures represent the ratios of NAg/Nmetal in precursors. Photographs of the chloroform solution containing OLA-AIS particles under UV light irradiation are shown in (c).
Non-stoichiometric AgInS2 (AIS) semiconductor particles were synthesized by the thermal decomposition of single-source precursors in solutions of two kinds of primary amines (oleylamine and octylamine). The Ag content in the resulting nanoparticles was controlled by adjusting the chemical composition of the precursor used, in which the mole ratio of Ag+ to total metal ions was varied from 0.1 to 0.7, resulting in the production of non-stoichiometric AIS particles with varying amounts of Ag vacancies. The average size of AIS particles was slightly decreased from 4.3 to 3.8 nm on changing the solvent from oleylamine to octylamine in the preparation, while the particle size seemed to be constant regardless of the content of Ag. On the other hand, the optical properties of AIS particles were considerably modified depending on the Ag content in the particles. The absorption onset was blueshifted from 750 to 580 nm with a decrease in the Ag content, due to the enlargement of the energy gap of particles. Intense photoluminescence originating from the donor-acceptor pair recombination was observed for each kind of AIS particle and then the photoluminescence peak wavelength was also blueshifted from 830 to 650 nm, being similar to the behavior of the absorption onset. The maximum photoluminescence quantum yield was ca. 70% for octylamine-modified AIS nanoparticles having a ratio of Ag+ to total metal ions of 0.37, which probably contained the optimum amount of Ag vacancies acting as the sites of donor-acceptor pair recombination with few surface defect sites for nonradiative recombination.